Như mọi người đã biết thì Spring Boot đã ra mắt phiên bản thứ 3 vào cuối tháng 11(24/11/2022) mang theo khá nhiều sự thay đổi, một trong số đó là Spring Security. Nếu như ở phiên bản Spring Security 5 chúng ta cấu hình Security bằng cách extends class WebSecurityConfigAdapter như sau:
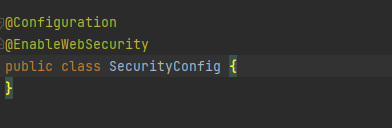
@Configuration@EnableWebSecuritypublicclassApplicationConfigextendsWebSecurityConfigurerAdapter{}thì ở phiên bản hiện tại class WebSecurityConfigAdapter đã không còn được Spring Boot hỗ trợ và bị xóa ra khỏi thư viện Spring Security 6. Điều này sẽ làm mọi người gặp khó khăn trong việc migrate từ Spring Boot 2.x lên Spring Boot 3,x, cũng như các anh em mới bắt đầu học về Spring Boot giống như mình Không thể nào cấu hình được Security khi xem các tutorial cũ. Chính vì vậy, trong bài viết ngày hôm nay mình sẽ chia sẻ cách cấu hình Spring Security 6 sử dụng Spring Boot 3.
Lưu ý: ở bài viết này mình dùng Spring Boot 3.0.2 là phiên bản mới nhất cho đến hiện tại
1. Cài đặt
Đầu tiên, chúng ta cài các thư viện cần thiết bao gồm: Spring Security và Spring Web và Lombok

Tiếp theo, tạo model Customer:
@Data@AllArgsConstructor@NoArgsConstructor@ToString@BuilderpublicclassCustomer{privateString id;privateString name;privateString phoneNumber;privateString email;}Vì bài này tập trung vào Security nên mình sẽ fake data và truyền thẳng vào controller như sau:
@RestControllerpublicclassCustomerController{finalprivateList<Customer> customers =List.of(Customer.builder().id("001").name("Customer 1").email("c1@gmail.com").build(),Customer.builder().id("002").name("Customer 2").email("c2@gmail.com").build());@GetMapping("/hello")publicResponseEntity<String>hello(){returnResponseEntity.ok("hello is exception");}@GetMapping("/customer/{id}")publicResponseEntity<Customer>getCustomerList(@PathVariable("id")String id){List<Customer> customers =this.customers.stream().filter(customer -> customer.getId().equals(id)).toList();returnResponseEntity.ok(customers.get(0));}}Như mọi người đã biết thì đôi khi chúng ta cũng sẽ có một số endpoint không cần authentication, cho nên ở đây mình sẽ thêm vào 1 function tên hello() không cần authen.
Ngoài ra mình cũng sẽ hard code bằng cách khai báo username và password trong application.properties:
spring.security.user.name=hach
spring.security.user.password=hacheery
Khi khởi động chương trình, trỏ vào đường dẫn http://localhost:8080/hello nó sẽ redirect vào trang login trước khi vào nội dung của trang web:
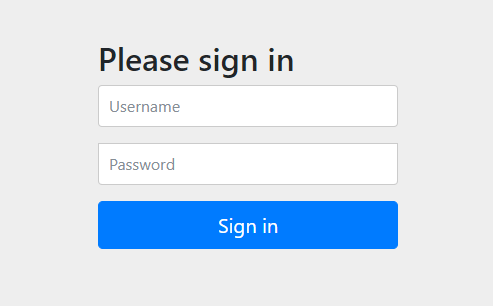
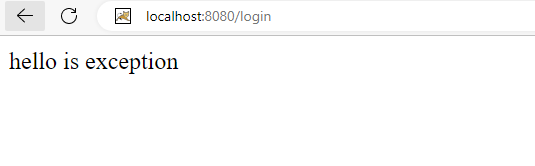
Sau khi login thành công sẽ redirect về trang hello:
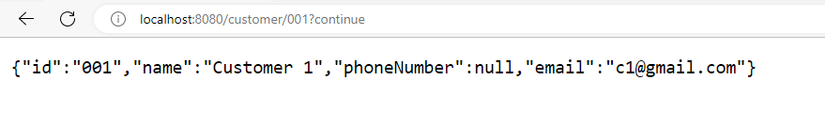
Tương tự với trang customer
2. Implement
Chúng ta sẽ tạo package config và class SecurityConfig để implement Spring Security 6.
Tiếp theo chúng ta sẽ thêm vào các annotation cần thiết khi config
Để tìm hiểu chi tiết hơn về các annotation thì mình xin gắn link bài viết mình đã từng đọc:
- Configuration: https://viblo.asia/p/spring-boot-6-atconfiguration-va-atbean-bJzKmyprK9N
- EnableWebSecurity: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/44671457/what-is-the-use-of-enablewebsecurity-in-spring#:~:text=The %40EnableWebSecurity is a marker,prompting for username and password.
Ở phiên bản Spring Security 5, khi implement WebSecurityConfigAdapter chúng ta có 2 override method nhận tham số truyền vào khác nhau.
- Thứ nhất là configure method với tham số là AuthenticationManagerBuilder. Ở đây chúng ta có thể khai báo thông tin của các user(user, password, role), và method này có liên quan đến authentication
@Overridepublicvoidconfigure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth)throwsException{// in-memory authentication
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("pankaj").password("pankaj123").roles("USER");// using custom UserDetailsService DAO
auth.userDetailsService(newAppUserDetailsServiceDAO());}- Thứ hai là configure method với tham số là HttpSecurity. Ở đây chúng ta có thể cấu hình web security cho các HTTP request cụ thể. Theo mặc định, nó sẽ được áp dụng cho tất cả các request, tuy nhiên chúng ta có thể tạo ra các ngoại lệ bằng cách sử dụng requestMatcher (requestMatcher) hoặc các phương thức tương tự khác. Và method này có liên quan đến authorization
@Overridepublicvoidconfigure(HttpSecurity http)throwsException{
http
.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/rest/**").authenticated().antMatchers("/**").permitAll().anyRequest().authenticated().and().csrf()//Disabled CSRF protection.disable();}Ở Spring Security 6, chúng ta có một số class mới thay thế như sau:
- Đối với việc khai báo thông tin của các user liên quan đến authentication chúng ta sẽ sử dụng interface UserDetailsService của Spring Security để khởi tạo bean. Sau khi khai báo thông tin của các user, vì bài viết này chỉ tập trung vào security config nên mình sẽ lưu data vào InMemory(Có một lưu ý nhỏ ở đây là password thì luôn cần được bảo mật và mã hóa nên mình sẽ khởi tạo thêm bean PasswordEncoder để encode password)
@Bean// authenticationpublicUserDetailsServiceuserDetailsService(PasswordEncoder encoder){UserDetails admin =User.withUsername("hach").password(encoder.encode("hacheery")).roles("ADMIN").build();UserDetails user =User.withUsername("user").password(encoder.encode("pwd1")).roles("USER").build();returnnewInMemoryUserDetailsManager(admin, user);}@BeanpublicPasswordEncoderpasswordEncoder(){returnnewBCryptPasswordEncoder();}- Đối với việc cấu hình web security cho các HTTP request, thì Spring Boot 3.0 đã tạo ra một method mới có tên là SecurityFilterChain để xử lý authorization . Như ở trên mình đã khai báo controller gồm 2 method là hello() và getCustomerList(), với method hello() mình sẽ để tất cả mọi người có thể truy cập vào mà không cần authentication và với method getCustomerList() mình sẽ yêu cầu authentication trước khi truy cập.
publicSecurityFilterChainsecurityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http)throwsException{return http.csrf().disable().authorizeHttpRequests().requestMatchers("/hello").permitAll()// với endpoint /hello thì sẽ được cho qua.and().authorizeHttpRequests().requestMatchers("/customer/**").authenticated()// với endpoint /customer/** sẽ yêu cầu authenticate.and().formLogin()// trả về page login nếu chưa authenticate.and().build();}Sau khi config thì chúng ta sẽ run để test xem config có hoạt động hay không. Đối với endpoint /hello sẽ không yêu cầu authenticate và đây là kết quả:
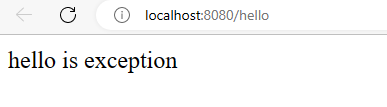
Đối với endpoint /customer/001 thì sẽ yêu cầu authenticate:
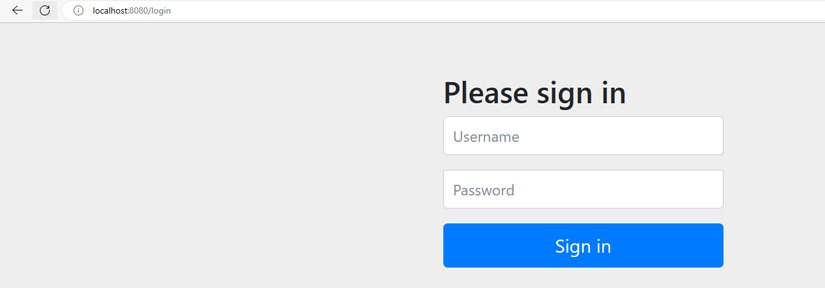
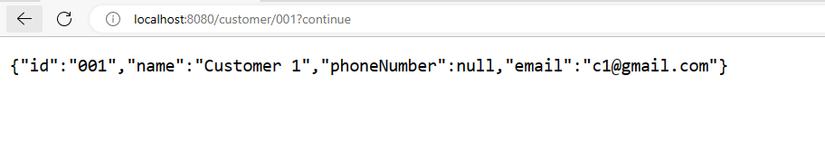
Và sau khi login thành công, chúng ta sẽ có được thông tin của customer 001:
Ở bài tiếp theo mình sẽ nói về việc phân quyền admin và user cũng như là login bằng user trong database. Hy vọng bài viết sẽ giúp ích cho mọi người trong việc config security trong spring boot 3.
Nguồn: viblo.asia