Bài viết tiếng việt – Liệt kê tài nguyên requests, limits trong Kubernetes một cách dễ dàng với kube-capacity CLI
When we work with Kubernetes, to check the resource requests and limits we will use kubectl describe, and to check the utilization of the resources we will use kubectl top. Today we will talk about the kube-capacity CLI that combines the two CLI above and provides an overview of the resource requests, limits, and utilization.
For example, the illustration.
Installation
On macOS, this project can be installed with Homebrew:
brew tap robscott/tap
brew install robscott/tap/kube-capacity
On Linux, we go to the releases page and select the appropriate Linux Package, for example with me:
curl -fsSLO https://github.com/robscott/kube-capacity/releases/download/v0.7.1/kube-capacity_0.7.1_Linux_x86_64.tar.gz
tar zxvf kube-capacity_0.7.1_Linux_x86_64.tar.gz
Move to one of the directories located in $PATH:
sudo mv kube-capacity /usr/local/bin/
Check if we have installed it successfully:
kube-capacity -h
...
Flags:
-a, --available includes quantity available instead of percentage used
-c, --containers includes containers in output
--context string context to use for Kubernetes config
-h, --help help for kube-capacity
--kubeconfig string kubeconfig file to use for Kubernetes config
-n, --namespace string only include pods from this namespace
--namespace-labels string labels to filter namespaces with
--node-labels string labels to filter nodes with
-o, --output string output format for information (supports: [table json yaml]) (default "table")
--pod-count includes pod count per node in output
-l, --pod-labels string labels to filter pods with
-p, --pods includes pods in output
--sort string attribute to sort results be (supports: [cpu.util cpu.request cpu.limit mem.util mem.request mem.limit name]) (default "name")
-u, --util include
Usage
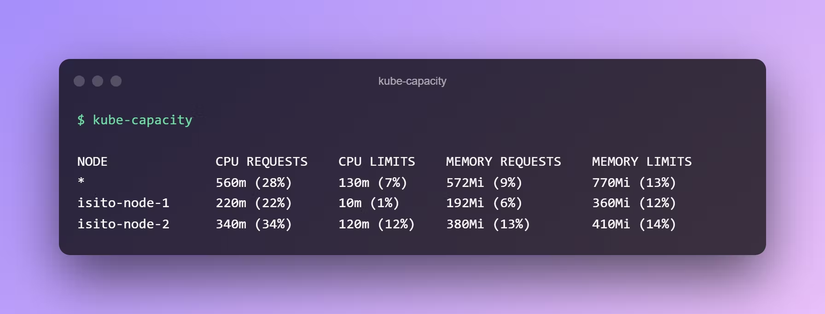
By default, kube-capacity will output a list of nodes with the total CPU and Memory resource requests and limits for all the pods running on them.
Default
For clusters with more than one node, the first line will also include cluster wide totals.
kube-capacity
NODE CPU REQUESTS CPU LIMITS MEMORY REQUESTS MEMORY LIMITS
* 560m (28%) 130m (7%) 572Mi (9%) 770Mi (13%)
isito-node-1 220m (22%) 10m (1%) 192Mi (6%) 360Mi (12%)
isito-node-2 340m (34%) 120m (12%) 380Mi (13%) 410Mi (14%)Including Pods
For more detailed output about the requests and limits of each Pod, add the flags --pods or -p to kube-capacity.
kube-capacity -p
NODE NAMESPACE POD CPU REQUESTS CPU LIMITS MEMORY REQUESTS MEMORY LIMITS
* * * 560m (28%) 780m (38%) 572Mi (9%) 770Mi (13%)
isito-node-1 * * 220m (22%) 320m (32%) 192Mi (6%) 360Mi (12%)
isito-node-1 istio-system istio-egressgateway-lwc6z 100m (10%) 200m (20%) 100Mi (3%) 200Mi (7%)
isito-node-1 istio-system istio-ingressgateway-7b5bcb98f8 120m (12%) 120m (12%) 92Mi (3%) 160Mi (5%)
isito-node-2 * * 340m (34%) 460m (46%) 380Mi (13%) 410Mi (14%)
isito-node-2 kube-system kube-proxy-3ki7 200m (20%) 280m (28%) 210Mi (7%) 210Mi (7%)
isito-node-2 tiller tiller-deploy 140m (14%) 180m (18%) 170Mi (5%) 200Mi (7%)Filtering By Namespace
To list by namespace, we use the flags --namespace or -n
kube-capacity -p -n istio-system
NODE NAMESPACE POD CPU REQUESTS CPU LIMITS MEMORY REQUESTS MEMORY LIMITS
isito-node-1 * * 220m (22%) 320m (32%) 192Mi (6%) 360Mi (12%)
isito-node-1 istio-system istio-egressgateway-lwc6z 100m (10%) 200m (20%) 100Mi (3%) 200Mi (7%)
isito-node-1 istio-system istio-ingressgateway-7b5bcb98f8 120m (12%) 120m (12%) 92Mi (3%) 160Mi (5%)Including Utilization
In case we need to check the utilization of the resources, we use the flags --util or -u.
Note: It’s important to note that this output relies on metrics-server functioning correctly in your cluster.
kube-capacity --util
NODE CPU REQUESTS CPU LIMITS CPU UTIL MEMORY REQUESTS MEMORY LIMITS MEMORY UTIL
* 560m (28%) 130m (7%) 40m (2%) 572Mi (9%) 770Mi (13%) 470Mi (8%)
isito-node-1 220m (22%) 10m (1%) 10m (1%) 192Mi (6%) 360Mi (12%) 210Mi (7%)
isito-node-2 340m (34%) 120m (12%) 30m (3%) 380Mi (13%) 410Mi (14%) 260Mi (9%)Sorting
To highlight the nodes, pods, and containers with the highest metrics, you can sort by a variety of columns:
kube-capacity --util --sort cpu.util
NODE CPU REQUESTS CPU LIMITS CPU UTIL MEMORY REQUESTS MEMORY LIMITS MEMORY UTIL
* 560m (28%) 130m (7%) 40m (2%) 572Mi (9%) 770Mi (13%) 470Mi (8%)
isito-node-2 340m (34%) 120m (12%) 30m (3%) 380Mi (13%) 410Mi (14%) 260Mi (9%)
isito-node-1 220m (22%) 10m (1%) 10m (1%) 192Mi (6%) 360Mi (12%) 210Mi (7%)Conclusion
This is a helpful tool when we need quickly check resource requests and limits.
Nguồn: viblo.asia