A short note about Containers Services on AWS. This post is a short note from the course Ultimate AWS Certified Solutions Architect Professional by Stephane Maarek. The only purpose of this post is a summary, if you want detailed learning, please buy a course by Stephane Maarek.

Containers Management on AWS
To manage containers, we need a container management platform:
- Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS): Amazon’s own container platform
- Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS): Amazon’s managed Kubernetes (open source)
- AWS Fargate: Amazon’s own Serverless container platform. Works with ECS and with EKS
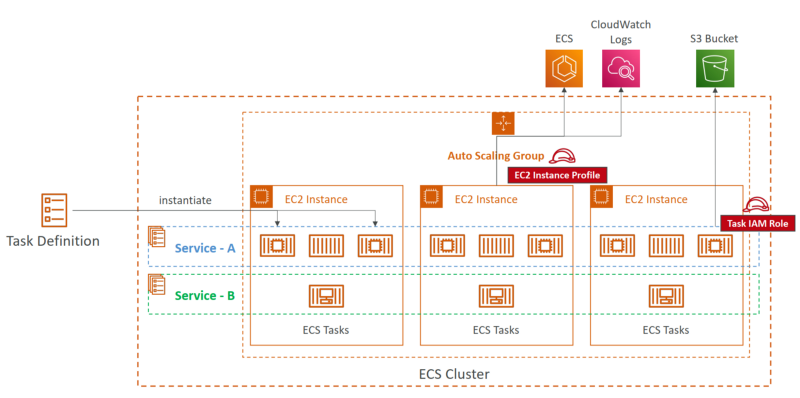
Amazon ECS
Concepts
ECS Cluster - logical grouping of EC2 instances.
ECS Service - defines how many tasks should run and how they should be run.
Task Definitions - metadata in JSON form to tell ECS how to run a Docker container (image name, CPU, RAM, …).
ECS Task - an instance of a Task Definition, a running Docker container(s).
ECS IAM Roles:
- EC2 Instance Profile - used by the EC2 instance (e.g., make API calls to ECS, send logs, …)
- ECS Task IAM Role - allow each task to have a specific role (e.g., make API calls to S3, DynamoDB, …)
Use cases
Run Microservices:
- Run multiple Docker containers on the same machine
- Easy Service Discovery features to enhance communication
- Direct integration with Application Load Balancer and Network Load Balancer
- Auto Scaling capability
Run Batch Processing / Scheduled Tasks.
Migrate Applications to the Cloud:
- Dockerize legacy applications running on-premises
- Move Docker containers to run on Amazon ECS
ALB Integration
We get Dynamic Port Mapping, allows you to run multiple
instances of the same application on the same EC2 instance. The ALB finds the right port on your EC2 Instances.
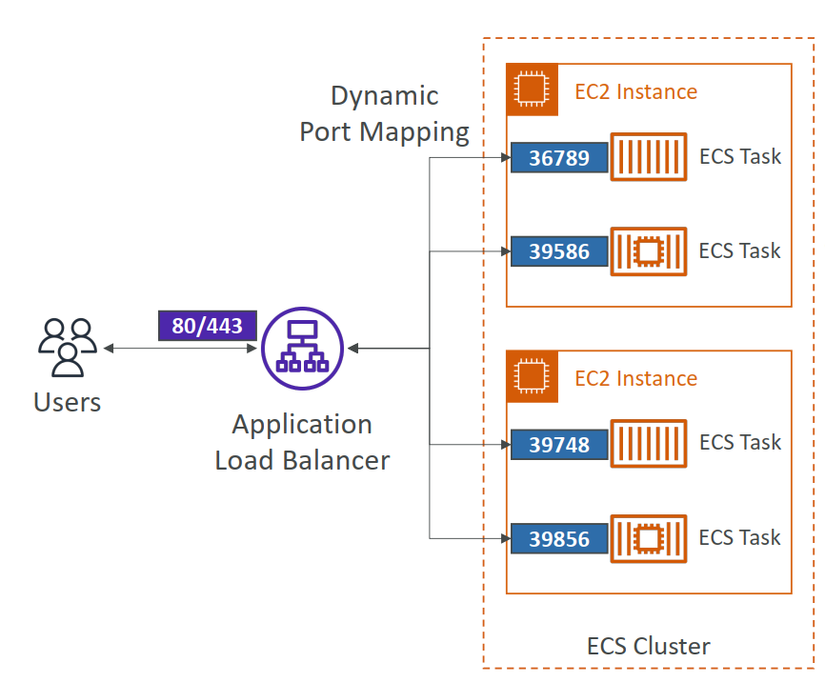
Use cases:
- Increased resiliency even if running on one EC2 instance
- Maximize utilization of CPU / cores
- Ability to perform rolling upgrades without impacting app uptime
Fargate
Launch Docker containers that without provision the infrastructure (no EC2 instances to manage). It’s all serverless!
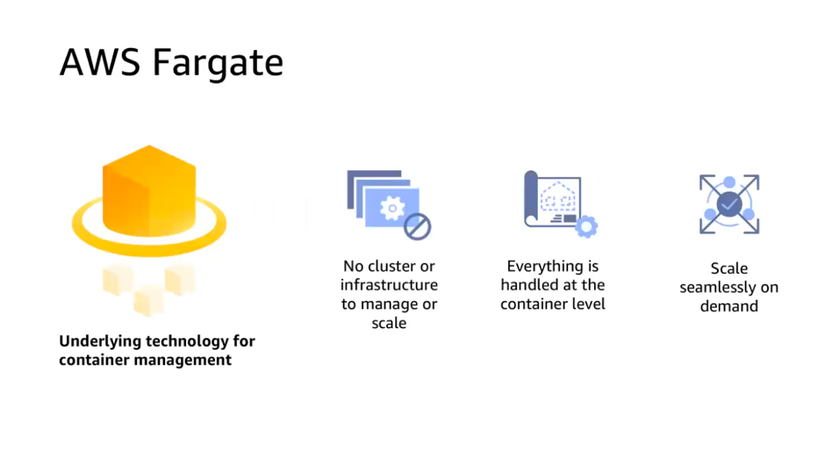
You create task definitions, and AWS runs containers for you based on the CPU/RAM you need. To scale, just increase the number of tasks. Simple! No more EC2 instances.
Security & Networking
You can inject secrets and configurations as Environment Variables into running Docker containers. Integration with SSM Parameter Store and Secrets Manager.
ECS Tasks Networking:
- none – no network connectivity, no port mappings
- bridge – uses Docker’s virtual container-based network
- host – bypass Docker’s network, uses the underlying host network interface
- awsvpc – Every tasks launched on the instance gets its own ENI and a private IP address. Simplified networking, enhanced security, Security Groups, monitoring, VPC Flow Logs. Default mode for Fargate tasks.
Service Auto Scaling
Automatically increase/decrease the desired number of tasks. CPU and RAM is tracked in CloudWatch at the ECS Service level.
Amazon ECS leverages AWS Application Auto Scaling:
- Target Tracking – scale based on target value for a specific CloudWatch metric
- Step Scaling – scale based on a specified CloudWatch Alarm
- Scheduled Scaling – scale based on a specified date/time (predictable changes)
Spot Instances
ECS Classic (EC2 Launch Type):
- Can have the underlying EC2 instances as Spot Instances (managed by an ASG)
- Instances may go into draining mode to remove running tasks
- Good for cost savings, but will impact reliability
AWS Fargate:
- Specify minimum of tasks for on-demand baseline workload
- Add tasks running on FARGATE_SPOT for cost-savings (can be reclaimed by AWS)
- Regardless of On-demand or Spot, Fargate scales well based on load
Elastic Container Registry
Store and manage container images on AWS, fully integrated with ECS, and access is controlled through IAM.
Two mode: Private and Public repository (Amazon ECR Public Gallery https://gallery.ecr.aws). Supports image vulnerability scanning, versioning, image tags, image lifecycle, …
End
End short note about AWS Containers Services.
Nguồn: viblo.asia