NoOne là bài crypto đầu tiên về 100 điểm trong vòng loại SV ATTT 2021. Bài này có sự pha trộn giữa web và crypto, cũng yêu cầu người chơi cần có khả năng đọc được code Python và hiểu được luồng xử lý của web.
Chính vì cần có sự hiểu biết cơ bản về cả 2 mảng web và crypto, nên nhiều bạn thấy cái là quay xe luôn 😅😂. Sau cuộc thi, khi mình đưa bài cho 1 số bạn làm thì: các bạn chỉ hay chơi crypto nhìn không hiểu gì, các bạn chỉ tập trung chơi mảng web thì không biết giải thế nào.
Tuy nhiên bài này không hề khó, chỉ ở mức dễ của web và dễ của crypto thôi.
1. Phân tích bài
Đề bài chỉ cho đường link đến 1 trang web với giao diện gồm 2 chức năng cơ bản là: đăng ký và đăng nhập. Khi đăng ký tài khoản cần điền: username, password và email.
Sau khi đăng ký tài khoản thành công và đăng nhập thì chúng ta sẽ được thấy giao diện chính của trang web. Tại đây thỉ có 2 bài blog dựng tạm cho có, kèm 1 trang /about và 1 trang /flag:
- /about: chứa source code của trang web.
- /flag: sẽ hiển thị flag khi đăng nhập với quyền admin.
Như vậy chúng ta sẽ cần phân tích source code của trang web, để từ đó có được quyền admin.
Source code có thể tải tại đây: source code noone
2. Phân tích source code
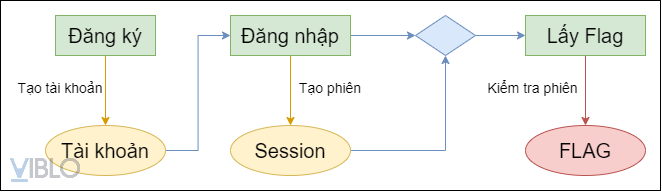
Để dễ theo dõi, mình đã vẽ lại sơ đồ các phần cần chú ý của như sau:
- Sơ đồ các bước để lấy flag:
- Sơ đồ xử lý của Server:
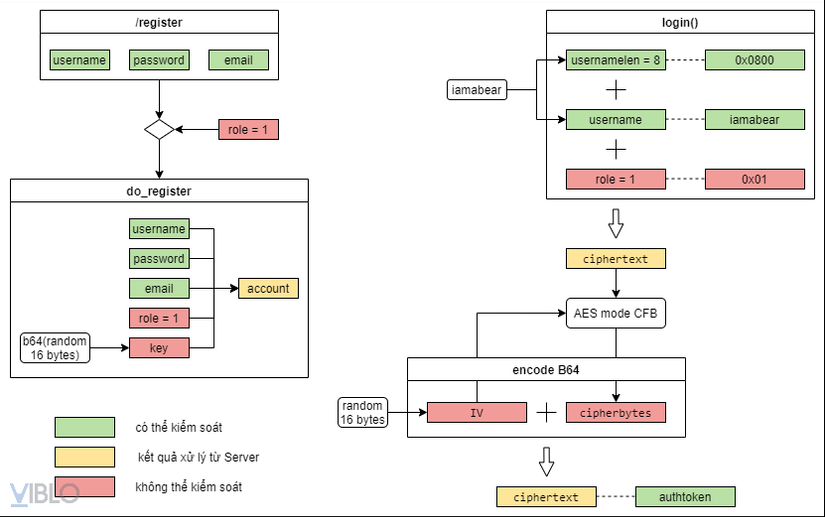
Trên sơ đồ xử lý của Server mình đã phân tích các chức năng cần phân tích, cùng với các tham số, giá trị,… Các thông tin trên sơ đồ đều được đánh dấu màu, chia thành 3 loại:
- Màu xanh lục: các giá trị do chúng ta nhập vào, hoặc giá trị chúng ta có thể kiểm soát, thay đổi.
- Màu vàng: các giá trị sinh ra do quá trình xử lý của Server
- Màu đỏ: các giá trị do server kiểm soát, chúng ta không thể thay đổi hay tác động vào.
Các bạn có thể lấy cái sơ đồ này để 1 bên, code để 1 bên. Vừa đọc code vừa nhìn sơ đồ thì sẽ dễ hiểu hơn 😀.
Khối chức năng đăng ký:
ROLE_ADMIN =0
ROLE_USER =1@app.route("/register", methods=('GET','POST'))defregister():if request.method =='POST':
username = request.form['username']
password = request.form['password']
email = request.form['email']
role = ROLE_USER
ifnot username ornot password:
flash('Username and Password is required!')else:
do_register(username, password, email, role)return redirect(url_for('login'))return render_template('register.html')defdo_register(username, password, email, role):
key = base64.b64encode(Random.new().read(AES.block_size))
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute('INSERT INTO users (username, password, email, role, encryptkey ) VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s, %s)',(username, password, email, role, key))
conn.commit()
cur.close()
conn.close()Khối chức năng đăng nhập:
@app.route("/", methods=('GET','POST'))deflogin():if request.method =='POST':
username = request.form['username']
password = request.form['password']ifnot username ornot password:
flash('Username and Password is required!')else:# verify login
user = verify_login(username, password)ifnot user:
flash('Username and Password is not correct!')else:
userid = user[0]
username = user[1]
role = user[5]# get key
key = base64.b64decode(user[4])# create authtoken
usernamebytes = username.encode('utf-8')
usernamelen =len(usernamebytes)
plainbytes =len(usernamebytes).to_bytes(2,"little")+ usernamebytes + role.to_bytes(1,"little")
ciphertext = encrypt(plainbytes, key)
response = make_response(redirect(url_for('index')))
response.set_cookie('userid',str(userid))
response.set_cookie('authtoken', ciphertext)return response
return render_template('login.html')defverify_login(username, password):
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute('SELECT id, username, password, email, encryptkey, role from users WHERE username = %s AND password = %s',(username, password))
user = cur.fetchone()
cur.close()
conn.close()return user
Khối chức năng kiểm tra quyền và đọc flag:
@app.route("/flag")@login_requireddefflag():
flag ="You are not admin"if g.role == ROLE_ADMIN:
flag ="xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"return render_template('flag.html', flag=flag)deflogin_required(f):@wraps(f)defwrap(*args,**kwargs):try:
ciphertext = request.cookies.get('authtoken')
userid = request.cookies.get('userid')ifnot ciphertext ornot userid:return redirect(url_for('login'))
encryptkey = get_encryptkey(userid)
plainbytes = decrypt(ciphertext, encryptkey)
usernamelen =int.from_bytes(plainbytes[:2],"little")
usernameencoded = plainbytes[2:usernamelen+2]
username = usernameencoded.decode("utf-8")
role = plainbytes[usernamelen+2]
g.username = username
g.role = role
except:
abort(401)return f(*args,**kwargs)return wrap
Khối chức năng mã hóa:
# input: bytes, output: base64 textdefencrypt(plainbytes, key):
iv = Random.new().read(AES.block_size)
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CFB, iv)
cipherbytes = cipher.encrypt(plainbytes)
ciphertext = base64.b64encode(iv + cipherbytes)return ciphertext
# input: base64 text, output: bytesdefdecrypt(ciphertext, key):
cipherbytes = base64.b64decode(ciphertext)
iv = cipherbytes[:AES.block_size]
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CFB, iv)
plainbytes = cipher.decrypt(cipherbytes[AES.block_size:])return plainbytes
3. Tìm hướng làm
Từ các sơ đồ và source code, chúng ta có thể phân tích như sau:
- Khi truy cập đường dẫn /flag, Server sẽ thực thi hàm login_required() để kiểm tra quyền của user. Nếu là admin thì sẽ trả về FLAG.
- Để kiểm tra quyền, Server sẽ thực hiện hàm decrypt(ciphertext, key). Với ciphertext là authtoken trả về sau khi login thành công, và key là giá trị encryptkey lấy trong CSDL.
- Do encryptkey được sinh ngẫu nhiên khi đăng ký tài khoản, nên chúng ta chỉ cần quan tâm tới cách Server tạo ra authtoken.
-
plainbytes =len(usernamebytes).to_bytes(2,"little")+ usernamebytes + role.to_bytes(1,"little") authtoken = encrypt(plainbytes)= encode base64 của [IV (16bytes sinh ngẫu nhiên)+ ciphertext (mã hóa AES mode CFB của plainbytes)] - Như vậy thì quyền của user được xác định bởi 1 byte cuối của authtoken.
- Do khi đăng ký thì mặc định chúng ta được gán quyền user, nên byte cuối sẽ có giá trị là 1.
- Để có quyền admin, chúng ta cần sửa byte cuối của authtoken trả về client từ 1 thành 0, sao cho server vẫn có thể giải mã được authtoken với khóa mã hóa lưu trong CSDL (lưu ý là chúng ta không biết giá trị của khóa này, do nó được sinh ngẫu nhiên và lưu trên Server).
Hướng làm đã có rồi, giờ thì chúng ta sẽ cần phân tích về thuật toán mã hóa mà Server xử dụng.
4. Phân tích thuật toán mã hóa
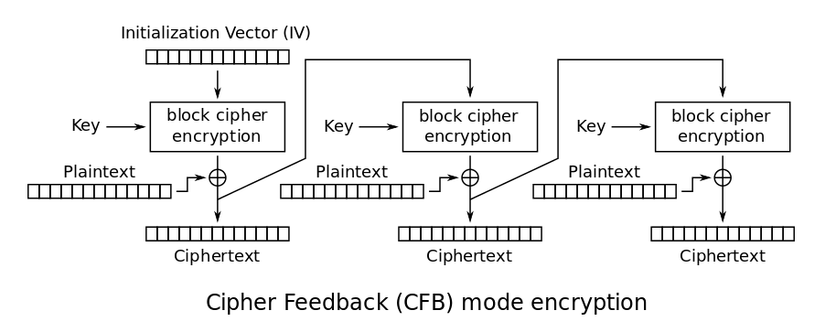
Server sử dụng thuật toán mã hóa AES mode CFB, có các tính chất sau:
- Là mã hóa khóa bí mật: quá trình mã hóa và giải mã đều dùng chung khóa.
- Là dạng mã hóa khối (block cipher): dữ liệu đầu vào sẽ được chia thành từng khối có kích thước đều nhau, sau đó mới tiến hành xử lý. Đối với thuật toán AES thì các khối có kích thước là 16 bytes.
- Mode CFB: khối đầu tiên được mã hóa bằng cách
Khối mã hóa 1 = (IV và Key) xor (Khối rõ 1). Từ khối thứ 2 trở đi được mã hóa bằng cách:Khối mã hóa thứ n = (Khối mã hóa thứ n-1 và Key) xor (Khối rõ thứ n). Sau khi tất cả các khối đã được mã hóa xong thì sẽ ghép các khối lại thành bản mã hóa hoàn chỉnh.
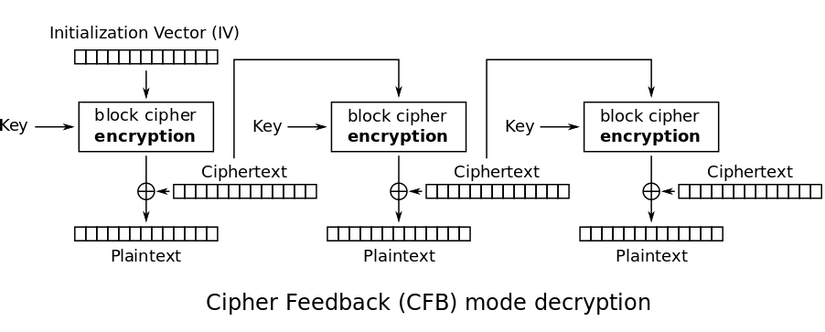
Quá trình giải mã: được thực hiện ngược lại với quá trình mã hóa.
Hình ảnh minh họa mode CFB (nguồn: wikipedia):
5. Hecker mode: ON 😎👾🤖💻🖱️
Quay lại với bài toán của chúng ta, giả sử toàn bộ đoạn plainbytes = len(usernamebytes).to_bytes(2, "little") + usernamebytes + role.to_bytes(1, "little") chỉ có độ dài 16 bytes thì chúng ta sẽ không bao giờ cần mã hóa tới block thứ 2.
Trong đoạn plainbytes này thì đã cố định 3 byte (2 bytes đầu tiên là độ dài username, 1 byte cuối là role user/admin) rồi. Chỉ cần username của chúng ta gồm 13 ký tự thì chắc chắn plainbytes sẽ có độ dài là 16 bytes, với 1 byte cuối xác định role user/admin.
Việc lấy username có độ dài đúng bằng 13 ký tự sẽ giúp chúng ta không cần quan tâm xem thuật toán AES sẽ xử lý thế nào khi block có độ dài < 16 bytes.
Vì chúng ta đã biết:
- Plaintext: được tạo thành từ username, độ dài username và role = 1.
và - Ciphertext: 16 bytes cuối của authtoken sau khi decode base64.
Ta có:
Ciphertext = (IV và Key) xor Plaintext
<=> (IV và Key) = Ciphertext xor Plaintext (1)
Từ (1) ta có:
New_Ciphertext = (IV và Key) xor New_Plaintext
<=> New_Ciphertext = (Ciphertext xor Plaintext) xor New_Plaintext
Như vậy là không cần quan tâm tới IV, không cần quan tâm tới Key, chúng ta có thể tạo ra Ciphertext mới, tương đương với authtoken mới chỉ từ nhứng thông tin đã biết.
6. Lấy Flag 🚩
Vậy thì chỉ cần viết 1 đoạn script để tạo ra authtoken mới, sau đó thay thế với giá trị authtoken cũ trong cookie của trang web. Rồi tải lại trang /flag là chúng ta sẽ có cờ của bài No One.

Script python:
import base64
# Python ngu không trực tiếp xor bytes với bytes được nên cần viết 1 hàm riêng (copy trên mạng về)defbitwise_xor_bytes(a, b):
result_int =int.from_bytes(a, byteorder="big")^int.from_bytes(b, byteorder="big")return result_int.to_bytes(max(len(a),len(b)), byteorder="big")
authtoken ='iHVcYuCO7VXUmvo+pb4XTs1NgMF6GhNkP+pCJ4aSYxU='
username ='iamabear11111'# 13 ký tự cho tiện, gộp vào đủ 16 bytes
role =1# role user
new_role =0# role admin
usernamebytes = username.encode('utf-8')# Plaintext cũ có role là user
plainbytes =len(usernamebytes).to_bytes(2,"little")+ usernamebytes + role.to_bytes(1,"little")# Plaintext mới có role là admin
new_plainbytes =len(usernamebytes).to_bytes(2,"little")+ usernamebytes + new_role.to_bytes(1,"little")# Lấy ra IV và ciphertext
iv = base64.b64decode(authtoken)[:16]
cipher = base64.b64decode(authtoken)[16:]
key_and_iv = bitwise_xor_bytes(cipher, plainbytes)
new_cipher = bitwise_xor_bytes(key_and_iv, new_plainbytes)
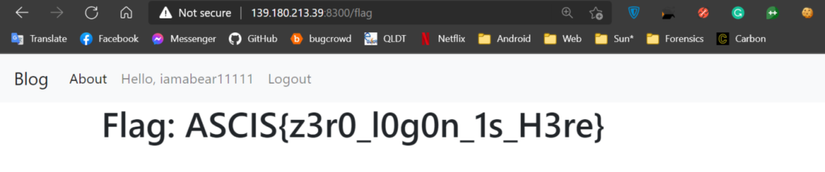
new_authtoken = base64.b64encode(iv + new_cipher)Sửa cookie và tải lại trang sẽ có Flag là: ASCIS{z3r0_l0g0n_1s_H3re}
Nguồn: viblo.asia