Tổng quan
Chúng ta đã học qua lí thuyết cơ bản ở phần một rồi, bây giờ bắt tay vào code thử 1 model đơn giản. Ở đây mình sẽ phân loại quần áo dựa trên bộ dữ liệu Fashion-MNIST.
MNIST thực sự khá tầm thường với các mạng neuron networks mà bạn có thể dễ dàng đạt được độ chính xác lớn hơn 97%. Fashion-MNIST là một tập hợp các hình ảnh quần áo có tỷ lệ 28×28 màu xám. Nó phức tạp hơn MNIST, vì vậy nó thể hiện tốt hơn hiệu suất thực tế trong mạng của bạn và thể hiện tốt hơn các tập dữ liệu mà bạn sẽ sử dụng trong thế giới thực.
Tiếp theo chúng ta cần phải đề ra phương hướng tiếp cận.
Phương hướng tiếp cận
Theo kinh nghiệm code gà của mình 😂 thì cách tiếp cận bài toán theo các bước sau đây :
B1. Thu thập, chuẩn bị dữ liệu
-
👍Có thể thu thập dữ liệu từ các nguồn có sắn trên mạng: dataset có sắn, crawl data,... -
👍Dùng GAN (Generative Adversarial Networks) để sinh thêm dữ liệu
B2. Xử lí, chuẩn hóa dữ liệu
-
👍 Augmentation data: resize, flip, affine,crop,... -
👍 Normalize data -
👍Chia làm 2 tập dữ liệu : training để huấn luyện và testing để kiểm tra kết quả
B3. Viết class Dataset, DataLoader
- Cái này mình sẽ giành phần riêng để nói về phần này. Các bạn có thể xem phần3 để hiểu thêm.
B4. Build model
-
👍 Xây dựng kiến trúc model -
👍 Viết hàm loss, optimizer. Có thể sử dụng hàm có sẵn cho khỏe
B5. Train model
-
👍 Viết hàm train -
👍 Train trên CPU hoặc GPU
B6. Test, visualize
Vì bài này đơn giản để tiếp cận pytorch nên mình chỉ code theo các bước sau:
-
👍 Load dữ liệu FASHION-MNIST -
👍 Build model -
👍 Train model -
👍 Test, visualize
Load dữ liệu FASHION-MNIST
Đầu tiên cần load dataset từ thư viện torchvision
import torch
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
import helper
# Define a transform to normalize the data
transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5,), (0.5,))])
# Download and load the training data
trainset = datasets.FashionMNIST('~/.pytorch/F_MNIST_data/', download=True, train=True, transform=transform)
trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)
# Download and load the test data
testset = datasets.FashionMNIST('~/.pytorch/F_MNIST_data/', download=True, train=False, transform=transform)
testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testset, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)
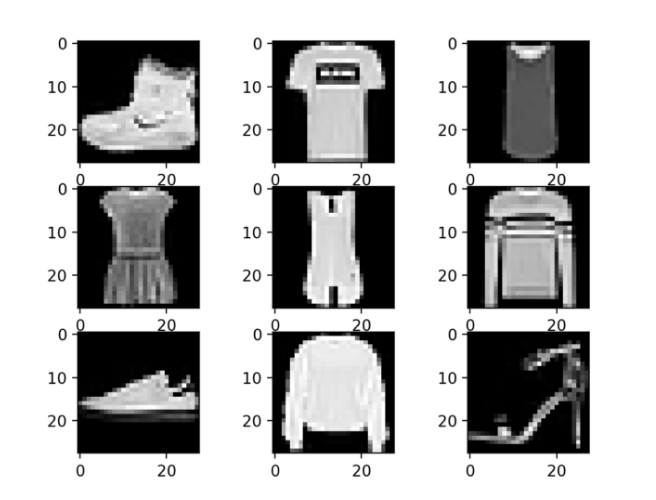
Tại đây bạn có thể xem một số bức ảnh trong dataset
# example of loading the fashion mnist dataset
from matplotlib import pyplot
# plot first few images
for i in range(9):
# define subplot
pyplot.subplot(330 + 1 + i)
# plot raw pixel data
pyplot.imshow(trainset[i], cmap=pyplot.get_cmap('gray'))
# show the figure
pyplot.show()

Build model
Import các thư viện cần thiết
import torch
from torch import nn, optim
import torch.nn.functional as F
Xây dựng kiến trúc mạng
# TODO: Define your network architecture here
class Classifier(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
# Because images is 28x28 which is a total of 784 pixels
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(784, 256)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(256, 128)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(128, 64)
# 10 classes
self.fc4 = nn.Linear(64, 10)
def forward(self, x):
# make sure input tensor is flattened
x = x.view(x.shape[0], -1)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc3(x))
x = F.log_softmax(self.fc4(x), dim=1)
return x
Train model
Đầu tiên bạn cần định nghĩa hàm loss (ví dụ như nn.CrossEntropyLoss hoặc nn.NLLLoss hoặc nn.MSELoss) và hàm optimizers (ví dụ như optim.SGD hoặc optim.Adam).
# TODO: Create the network, define the criterion and optimizer
model = Classifier()
criterion = nn.NLLLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.003)
Sau đó viết hàm train
# TODO: Train the network here
epochs = 5
def train():
for e in range(epochs):
running_loss = 0.0
for images, labels in trainloader:
log_ps = model(images)
loss = criterion(log_ps, labels)
optimizer.zero_grad() # cần xóa gradient sau mỗi vòng lặp để tránh chồng chất gradient vì đạo hàm hàm hợp của backpropagation
loss.backward() # backpropagation process
optimizer.step() # update weights
running_loss += loss.item()
else:
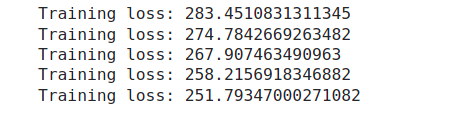
print(f"Training loss: {running_loss/len(trainloader)}")
Quá trình training
Test , visualize
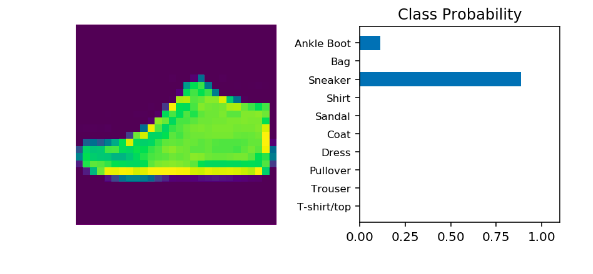
Visualize kết quả
%matplotlib inline
%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'retina'
import helper
# Test out your network!
dataiter = iter(testloader)
images, labels = dataiter.next()
img = images[1]
# TODO: Calculate the class probabilities (softmax) for img
ps = torch.exp(model(img))
# Plot the image and probabilities
helper.view_classify(img, ps, version='Fashion')
Exercise
Link all code : https://github.com/trungtruc123/Pytorch/blob/master/intro-to-pytorch/Part 4 – Fashion-MNIST (Solution).ipynb
Các bạn có thể tải 8 bài tập từ link để làm. Bài tập gồm 2 phần exercises và solutions. Làm exercise xong mới quay lại xem đáp án nhé 😂.
Chúc các bạn thành công!
Nguồn: viblo.asia