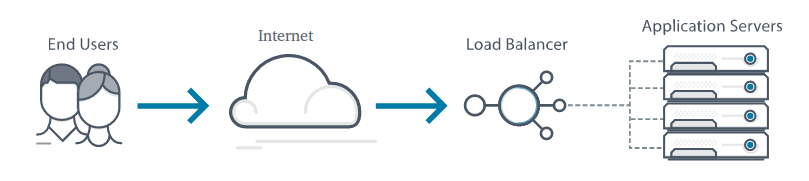
Load balancing is the mechanism of distributing network traffic across multiple servers. This ensures no single server takes too much pressure and memory. By spreading the work evenly, load balancing improves application scalability. It also boost up the chance of availability of applications to users. Load balancers are part of modern application life cycle. Over time, software load balancers have added additional capabilities including security that made it more important thing to study.
Background
In computing world, Scalability is a term that ensures normal experience of an application with the increase of users involved. Usually in a system, if number of user, and eventually user interaction increases, there is a chance of processing machine being busy and so results in a unstable application. As a result, user experience downgrades as the processing time become higher. So knowing about scaling and applying them is a must. We can two kinds of scaling in our computing world –
- Horizontal scaling: This type asks to change the number of processing node(such as computers) in the system. Its a fast, feasible scaling technique, but the problem is data inconsistency.
- Vertical scaling: This type asks to updrade the node in the system. Its a data consistent system but the problem is sometimes it is not feasible in real world.
We will talk about only horizontal scaling next. As load balancing lie on that type.
Load Balancing
Load balancing is the most hit and go method of scaling out server infrastructure. As application popularity increases, new nodes can be easily added to the server pool, and the load balancer will immediately begin sending traffic to the new machine. A load balancer works between the client and the server pool accepting incoming network and application traffic and distributing the traffic across multiple backend servers using various methods. By balancing application requests across multiple servers, a load balancer reduces load in a single server and protects application server from creating a single point of failure, thus improving overall application availability and responsiveness.
How Load Balancer Works
When one application server fails for some reason, the load balancer directs all new application requests to other available machines in the server. To handle more advanced application delivery requirements, an application delivery controller (ADC) is used to improve the performance, security and resiliency of applications delivered to the web. An ADC is not only a load balancer, but a platform for delivering networks, applications and mobile services in the fastest, safest and most consistent manner, regardless of place, time and access m.
Load Balancing Algorithms
Load balancing uses various algorithms. Different load balancing algorithm gives different benefits. Use of anyone of these varies on application owners need. Some examples are following –
- Round Robin Method: This method rotates servers by sending traffic to the first available server and then moves that server to the bottom of the queue.
- Least Connection Method: It selects the server with the fewest active connections. This method works well when there are a large number of permanent connections in the traffic unevenly distributed between the servers.
- The Least Response Time Method: This method selects the service with the fewest active connections and the lowest average response time.
- The Least Bandwidth Method: This method directs traffic to the server that is currently serving the least amount of traffic, measured in megabits per second (Mbps).
- IP Hash: the IP address of the client determines which server receives the latest incoming request.
Hope this post will make you more interested about load balancer. Please study further to know more. Thank you
References:
Nguồn: viblo.asia