Problem-31
Nếu head của linked list trỏ đến phần tử thứ k, thì bạn sẽ lấy các phần tử trước phần tử thứ k như thế nào?
Solution:
Sử dụng Memory Efficient Linked Lists [XOR Linked Lists].
Problem-32
Với hai linked list đã được sắp xếp, chúng ta cần hợp nhất chúng thành danh sách thứ ba theo thứ tự đã sắp xếp.
Solution:
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {
if(head1 == null) {
return head2;
}
if(head2 == null) {
return head1;
}
ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
if(head1.getData() <= head2.getData()) {
head = head1;
head.setNext(mergeTwoLists(head1.getNext(), head2));
} else {
head = head2;
head.setNext(mergeTwoLists(head2.getNext(), head1));
}
return head;
}
Time Complexity – O(n).
Problem-33
Chúng ta có thể giải quyết Problem-32 mà không cần đệ quy không?
Solution:
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode curr = head;
while(head1 != null && head2 != null) {
if(head1.getData() <= head2.getData()) {
curr.setNext(head1);
head1 = head1.getNext();
} else {
curr.setNext(head2);
head2 = head2.getNext();
}
}
if(head1 != null) {
curr.setNext(head1);
} else if(head2 != null) {
curr.setNext(head2);
}
return head.getNext();
}
Time Complexity – O(n).
Problem-34
Đảo ngược danh sách liên kết theo cặp.
Nếu bạn có danh sách liên kết chứa 1→2→3→4→X1 → 2 → 3 → 4 → X, thì sau khi hàm được gọi, danh sách liên kết sẽ giữ 2→1→4→3→X2 → 1 → 4 → 3 → X.
Solution:
//Phiển bản Đệ quy
public static ListNode ReversePairRecursive(ListNode head) {
ListNode temp;
if(head == null || head.getNext() == null) {
return null;
} else {
//Reverse first pair
temp = head.getNext();
head.setNext(temp.getNext());
temp.setNext(head);
head = temp;
//Call the method recursively for the rest of the list
head.getNext().setNext(ReversePairRecursive(head.getNext().getNext()));
return head;
}
}
//Phiển bản Vòng lặp
public static ListNode ReversePairIterative(ListNode head) {
ListNode temp1 = null;
ListNode temp2 = null;
while(head != null && head.getNext() != null) {
if(temp1 != null) {
temp1.getNext().setNext(head.getNext());
}
temp1 = head.getNext();
head.setNext(head.getNext().getNext());
temp1.setNext(head);
if(temp2 == null) {
temp2 = temp1;
}
head = head.getNext();
}
return temp2;
}
Time Complexity – O(n).
Space Complexity – O(1).
Problem-35
Cho một cây nhị phân, hãy chuyển đổi nó thành danh sách liên kết kép.
Solution:
Mình sẽ trình bày chi tiết trong chương về Trees.
Problem-36
Làm thế nào để sắp xếp các Linked Lists?
Solution:
Mình sẽ trình bày chi tiết trong chương về Sorting.
Problem-37
Nếu chúng ta muốn nối hai danh sách liên kết, cách nào sau đây cho độ phức tạp O (1)?
- Singly linked lists
- Doubly linked lists
- Circular doubly linked lists
Solution:
Circular Doubly Linked Lists. Điều này là do đối với danh sách liên kết đơn và kép, chúng ta cần xem qua danh sách đầu tiên cho đến cuối và nối danh sách thứ hai. Nhưng trong trường hợp danh sách được liên kết kép vòng, chúng ta không phải duyệt qua danh sách.
Problem-38
Chia một Circular Linked List thành hai phần bằng nhau. Nếu số lượng nút trong danh sách là số lẻ thì hãy đặt danh sách đầu tiên thừa một nút so với danh sách thứ hai.
Solution:
Algorithm
- Lưu trữ con trỏ giữa và con trỏ cuối cùng của danh sách liên kết vòng bằng cách sử dụng thuật toán tìm chu trình Floyd.
- Làm cho nửa thứ hai của vòng.
- Làm cho nửa thứ nhất của vòng.
- Đặt con trỏ đầu của hai linked lists.
Ví dụ, xem Circular Linked List sau:
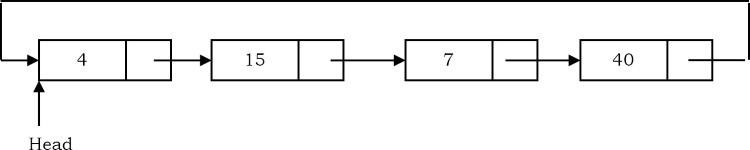
Sau khi chia ra nó thành như sau:
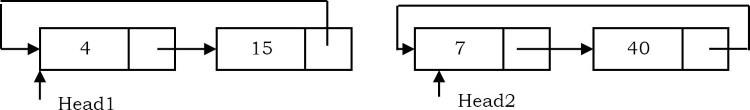
public static void splitList(ListNode head, ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {
ListNode slowPtr = head, fastPtr = head;
if(head == null) return;
while(fastPtr.getNext() != head && fastPtr.getNext().getNext() != head) {
fastPtr = fastPtr.getNext().getNext();
slowPtr = slowPtr.getNext();
}
//If there are even elements in list then move fastPtr
if(fastPtr.getNext().getNext() == head) {
fastPtr = fastPtr.getNext();
}
//Set the head pointer of first half
head1 = head;
//Set the head pointer of the second half
if(head.getNext() != head) {
head2 = slowPtr.getNext();
}
//Make second half circular
fastPtr.setNext(slowPtr.getNext());
//Make first half circular
slowPtr.setNext(head);
}
Time Complexity – O(n).
Space Complexity – O(1).
Problem-39
Làm sao để kiểm tra một Linked List xuôi ngược đều giống nhau.
Solution:
Algorithm
- Lấy giữa danh sách liên kết.
- Đảo ngược nửa sau của danh sách liên kết.
- So sánh nửa đầu và nửa sau.
- Xây dựng danh sách liên kết ban đầu bằng cách đảo ngược nửa sau một lần nữa và nối nó
trở lại nửa đầu
Time Complexity – O(n).
Space Complexity – O(1).
Problem-40
Trao đổi các phần tử liền kề trong một danh sách liên kết.(Giống Problem 34)
Solution:
public static ListNode exchangeAdjacentNodes(ListNode head) {
ListNode temp = new ListNode(0);
temp.setNext(head);
ListNode prev = temp, curr = head;
while(curr != null && curr.getNext() != null) {
ListNode tmp = curr.getNext().getNext();
curr.getNext().setNext(prev.getNext());
prev.setNext(curr.getNext());
curr.setNext(tmp);
prev = curr;
curr = prev.getNext();
}
return temp.getNext();
}
Time Complexity – O(n).
Space Complexity – O(1).
Nguồn: viblo.asia