I. What is Middleware? why so important?
When we are working on a real application, when we often require processing operations that need time to respond (asynchronous operations to get data from the api or operations to read and write files …) . This operations, we call it as side effects in functional programming. Anyway in redux, we have some constraints:
- Processes in Reducers must be synchronous and pure functions, returning new state.
- Reducers will not use async functions because the global state cannot be changed.
So if we need be able to deal with side effects, we need to do it in the middeware.
II. Middleware in Redux!
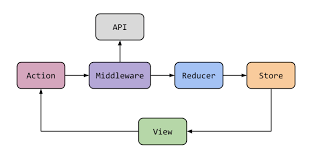
In Redux, middleware is the layer between Reducers and Dispatch Actions, it will be called before the action is dispatched. Currently we have some options for middleware libraries for redux. But the most famous and normally used are redux-saga, redux-thunk and redux-observable.
The 3 libraries above, they can solve most of the cases that we face in Redux. Although redux thunk is quite easy to understand and coding, it is not very good in some situations, this is overcome with more powerful libraries like redux saga and redux observale.
III. How Redux saga working?
For easy to understand, how redux saga works we need to understand some basic concepts like generator function. Generator function is a function capable of deferring execution while preserving the context. It’s a bit confusing, in simple terms, a generator function is a function that has the ability to pause before the function ends (different from a pure function that will execute all statements in the function when called), and can continue continue running at another time. It is this new function that helps us to solve the asynchronous problem, the function will stop and wait for async to finish running and then continue executing.
The Redux saga provides effect helper functions, which return an effect object that contains special information that instructs the Redux middeware to perform other actions. The helper effect functions will be executed in the generator functions.
Some helpers in the redux saga:
- takeEvery() : executes and returns the result of every action called.
- takeLastest() : means if we perform a series of actions, it will only execute and return the result of the last action.
- take() : pause until action is received
- put() : dispatch an action.
- call(): call function. If it returns a promise, pause the saga until the promise is resolved.
- race() : run multiple effects simultaneously, then cancel them all if one of them ends
IV. Small app
For understanding more, we will create a small app how to implement redux saga in Project. We will do a function to take all Book from server. To execute a Saga, we first need to create an action. In the bookSlice.js file, we add the following code:
import { createSlice } from '@reduxjs/toolkit';
import { all } from 'redux-saga/effects';
import { createSagaAction } from '~/utils';
import { fetchBooks } from './BookAPI';
const initialState = {
loading: true,
books: [],
page: {
total_pages: 0,
current: 1,
},
};
export const getBookList = createSagaAction(
'book/getBookList',
async (payload) => {
const { data } = await fetchBooks(payload);
return { data };
}
);
export function* bookSaga() {
yield all([getBookList.saga()]);
}
export default bookSlice.reducer;
We create a function to get the book data from the api and put it in the file BookAPI.js
import axios from 'axios';
const MAX_SIZE = 20;
export function fetchBooks(options = {}) {
const url = ...
return axios.get(url);
}
You create a new file saga.js and add the following code to be able to add an asynchronous action when the fetchData action executes:
import { all } from 'redux-saga/effects';
import { bookSaga } from '~/features/book/BookSlice';
export function* rootSaga() {
yield all([
bookSaga(),
]);
}
Run the application and we will get a list of books that we can push to view.
Nguồn: viblo.asia